Weak April Jobs Report Reflects Canadian Lockdown
Canada’s jobs recovery impaired by third-wave virus restrictions

This morning, Statistics Canada released the April 2021 Labour Force Survey showing a major deterioration in the jobs market following the third-wave COVID containment measures. Employment fell by 207,100 (-1.1%) in April, and the unemployment rate rose 0.6 percentage points to 8.1%.
Employment declined in both full-time (-129,000; -0.8%) and part-time (-78,000; -2.3%) work. The number of employed people working less than half their usual hours increased by 288,000 (+27.2%).
The number of Canadians working from home grew by 100,000 to 5.1 million.
Total hours worked fell 2.7% in April, driven by declines in educational services, accommodation and food services, and retail trade.
The labour underutilization rate, which captures the full range of available people who want to work, rose 2.3 percentage points to 17.0% in April.
The number of Canadians unemployed for 27 weeks or more—the long-term unemployed–increased to 486,000. This group might well be the most scarred by the pandemic in terms of their job prospects and skill deterioration.
Hardest hit by industry sector
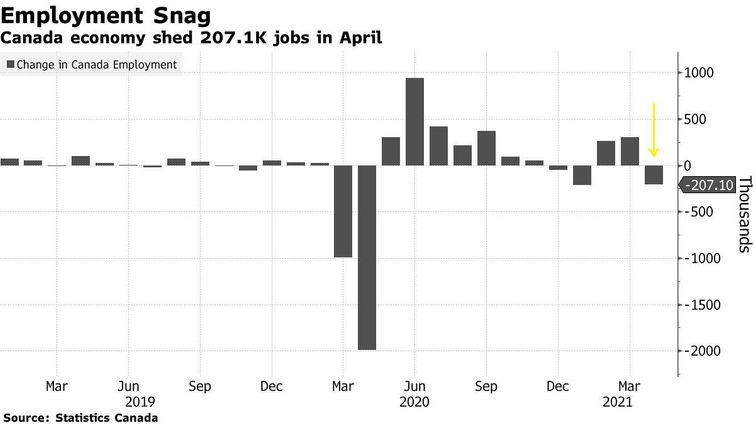
In April, employment fell in several industries directly impacted by public health restrictions, namely retail trade (-84,000); accommodation and food services (-59,000); and information, culture and recreation (-26,000).
Accommodation and food services accounted for more than two-thirds (70.9%) of the overall employment gap (-503,000) compared with February 2020.
Employment increased in public administration (+15,000); professional, scientific and technical services (+15,000); and finance, insurance and real estate (+15,000), three industries where many activities can be performed remotely.
Employment in goods-producing industries was little changed in April.
Fewer people working in Ontario and British Columbia
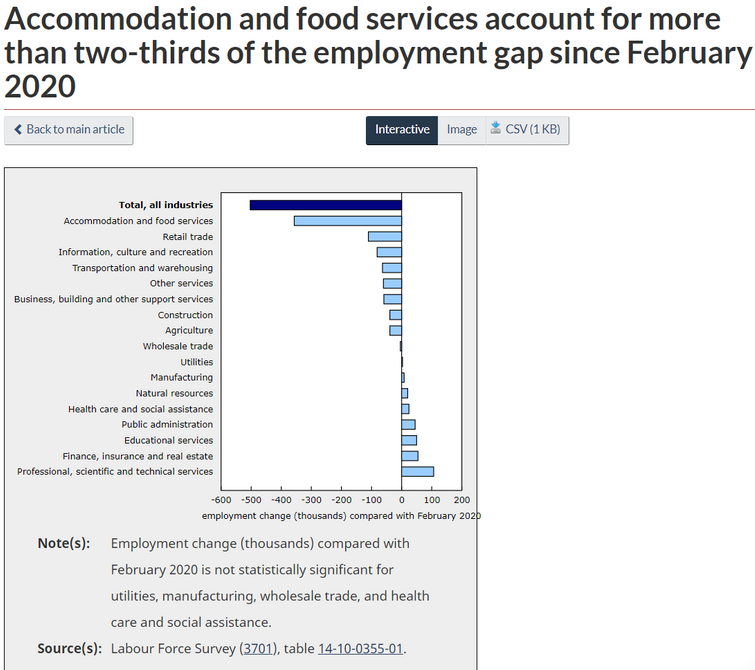
Following gains over the previous two months, employment in Ontario fell 153,000 (-2.1%) in April.
Employment in British Columbia declined by 43,000 (-1.6%)—the first decrease since substantial employment losses in March and April 2020.
Employment increased in Saskatchewan and New Brunswick, while there was little change in all other provinces.
Bottom line
The third wave restrictions cut heavily into Canadian employment in April, mostly in line with expectations. However, in contrast to the mild impact on growth from second-wave restrictions, the latest drop may leave more of a mark on the broader economy, with full-time positions also hit this time. On a less downbeat note, the employment-to-population rate remains a full point above January’s level (at 59.6%). The participation rate is also higher than in the second wave at 64.9% (albeit down a bit from the pre-pandemic trend of 65.5%).
Looking ahead, as in prior waves of virus spread, employment will rebound once the government can ease containment measures. And that light at the end of the tunnel is getting closer, with vaccination rates ramping up. In the meantime, government support programs for those losing work remain in place and help put a floor under household purchasing power.
Canada’s economy remains about half a million jobs shy of pre-pandemic levels. The Canadian dollar rose to 82.36 cents US after the report. The yield on Canada’s five-year bond yield dipped to 0.894%, down a few ticks from Thursday’s close.
The U.S. Labor Department also released soft jobs data Friday that were even more disappointing. U.S. payrolls increased by just 266,000, versus estimates for a 1 million gain.
Dr. Cooper is Chief Economist of Dominion Lending Centres, Canada’s leading mortgage and leasing company with more than 2,600 members offering free expert advice across the country. In this role, Dr. Cooper helps Canadians understand the issues surrounding their most important financial decision— buying a home.
Named “the megawatt celebrity economist” by Canada’s national newspaper—and repeatedly cited as one of the most influential women in Canada, Dr. Cooper served as Chief Economist and Executive Vice-President of BMO Financial Group where she was responsible for global economic and financial forecasting as well as country-risk and industry-risk analysis. She joined BMO Financial Group in 1994 when it acquired Burns Fry, where she had been Chief Economist, Co-Head of Fixed Income and the first female director of a Bay Street investment firm.
Dr. Cooper has an M.A. and Ph.D. in Economics from the University of Pittsburgh. She began her career at the Federal Reserve Board in Washington, D.C. where she worked very closely with then-Chairman, Paul Volcker and subsequently joined the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae) as Director of Financial Economics.








